Ultimate Guide to Running Quantized LLMs on CPU with LLaMA.cpp

We are all witnessing the rapid evolution of Generative AI, with new Large Language Models (LLMs) emerging daily at various scales. However, running these models on local machines remains a challenge due to their high computational demands. LLaMA.cpp solves this problem by enabling the use of quantized models, which are significantly lighter while maintaining reasonable accuracy.
Llama.cpp is a light weight, open-source library, which was developed by Georgi Gerganov to enable LLMs inference possible on local machine. It supports running quantized models which are lower in precision and light in weight reducing memory requirements significantly. This allows efficient execution of LLMs without needing specialized hardware.
Running LLaMA.cpp using command line
Steps to Run Inference with LLaMA.cpp
- Clone and build Llama.cpp.
- Download Quantized(GGUF) model of your choice.
- Run Inference.
Step 1: Install CMake (Required for Building LLaMA.cpp)
Make sure that cmake is installed. If not, run following commands to install

Step 2: Clone and Build LLaMA.cpp

Once the cloning is completed, build llama.cpp using:

Step 3: Download a GGUF Quantized Model
Download the GGUF quantized model of your choice. Remember, The lower the quantization bit, the faster the model, but with reduced accuracy. Here 4 bit Small version of Mistral-7B-Instruct is used.
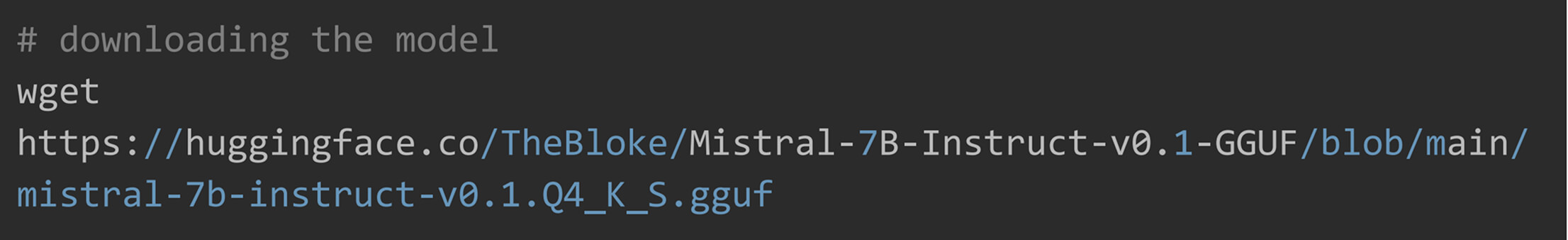
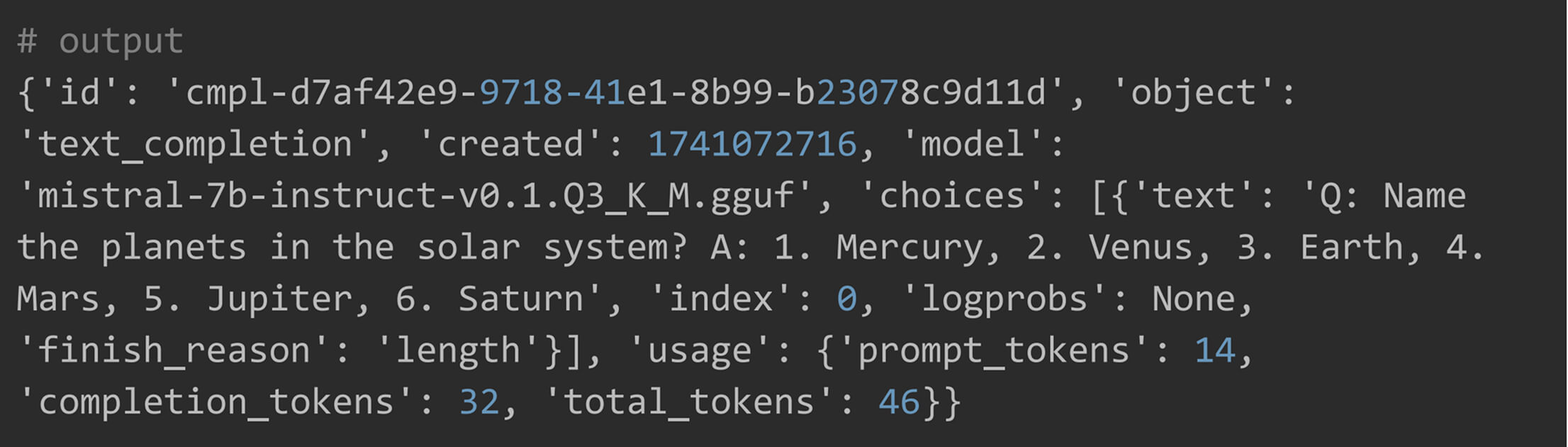
Step 4: Run Inference
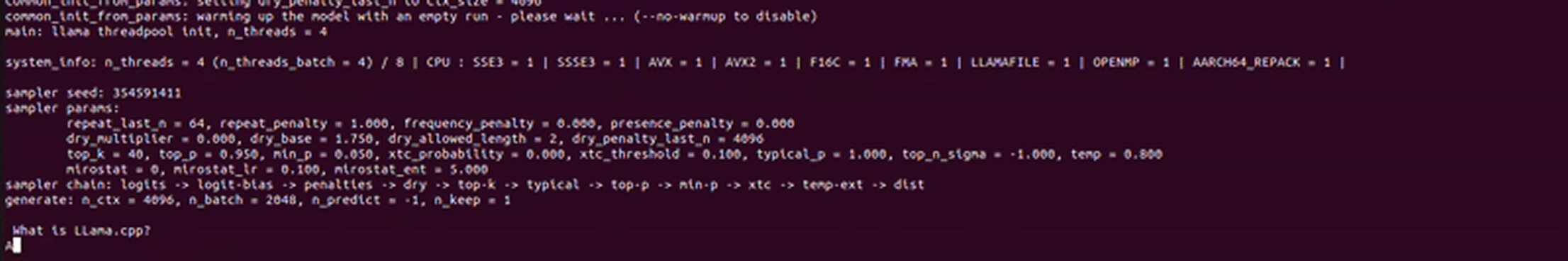
After downloading the model you can run the inference. Make sure to pass the correct path of model.

Here is the output.
Running LLaMA.cpp with Python Bindings
LLaMA.cpp provides bindings for different programming languages, allowing easy integration of quantized LLMs into applications. Here, we explore python bindings.
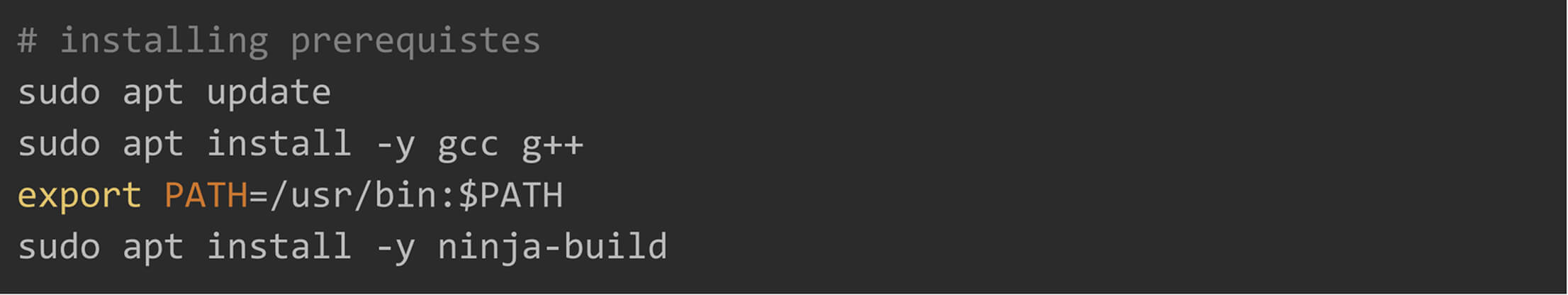
Install Dependencies and Python Binding
Before installing the python bindings, ensure your system has the necessary tools.

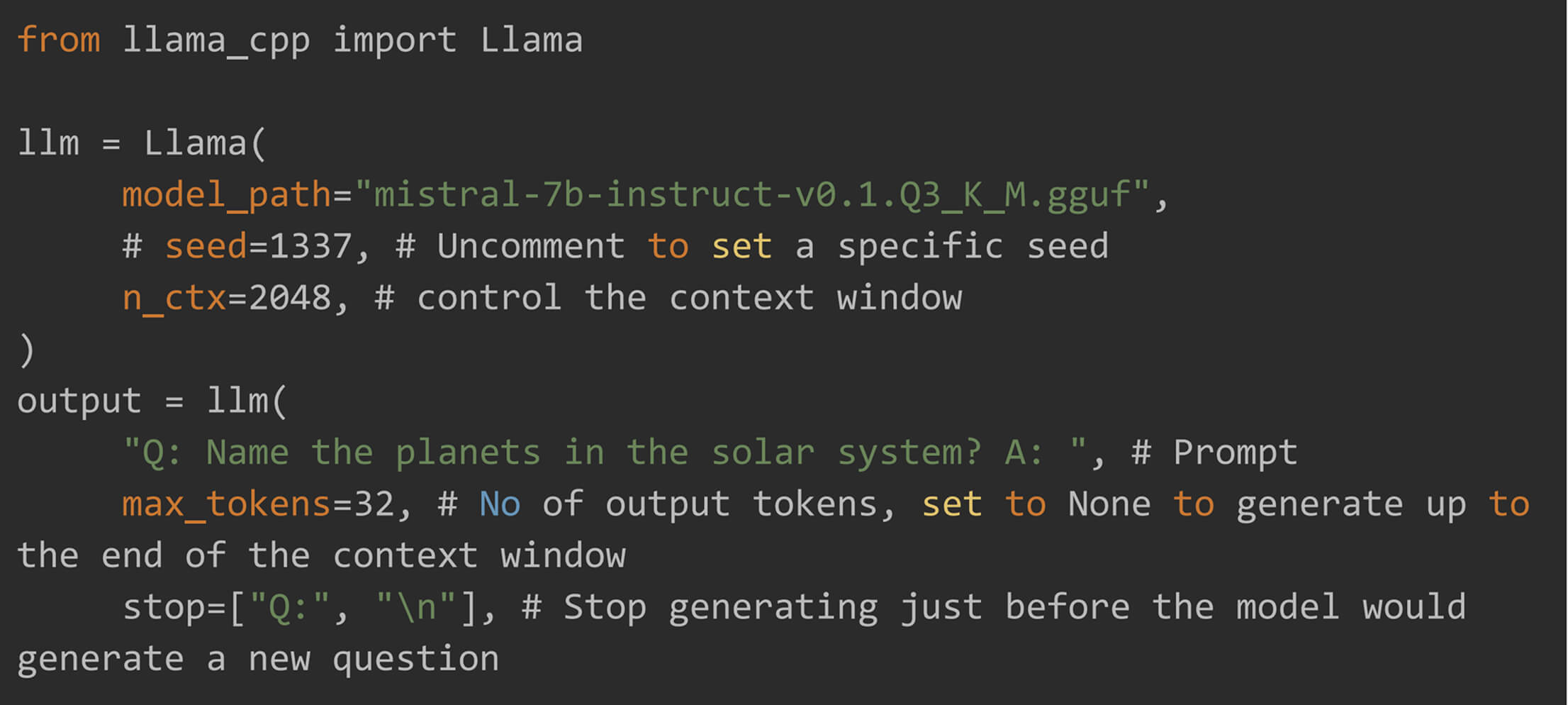
Text Generation
Make sure that cmake is installed. If not, run following commands to install

Creating Embedding with LLaMA.cpp

Running Multimodal Vision LLMs in LLaMA.cpp
LLaMA.cpp now supports list of opensource multi-modals as well through quantization. Unlike simple LLMs, llama.cpp python have separate wrappers for each vision mode. You can find list of model and their chat-handler here.
In this guide, we will be using MiniCPM, an opensource MLLM, which is supported in llama.cpp.
Understanding the Required Models
To run Vision LLMs, you need to download two models:
- This is the main language model.
- Different quantized versions (e.g., Q3_K_L, Q4_K_M) are available for optimized performance.
- This acts as a bridge between the image encoder and the LLM.
- It translates images into a format the LLM can understand.
- These models are usually not quantized and available only in full precision (fp16).
Step 1: Download the Required Models
Download both GGUF (quantized) and MMProj (full precision) models from Hugging Face.


Step 2: Load the Models
Provided mmproj models path to Chat handler and gguf models path to Llama.


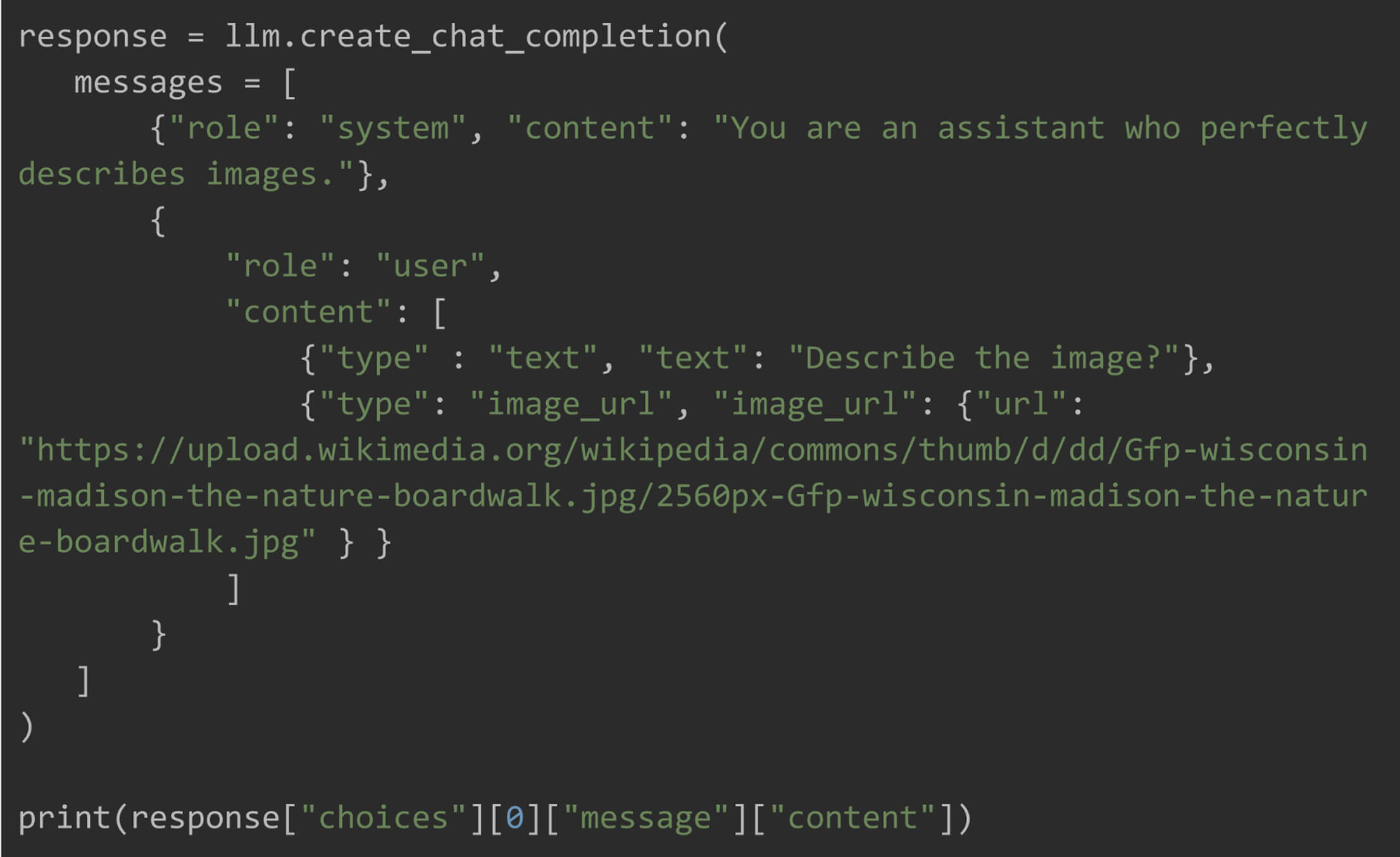
Step 3: Generate a Response for an Image

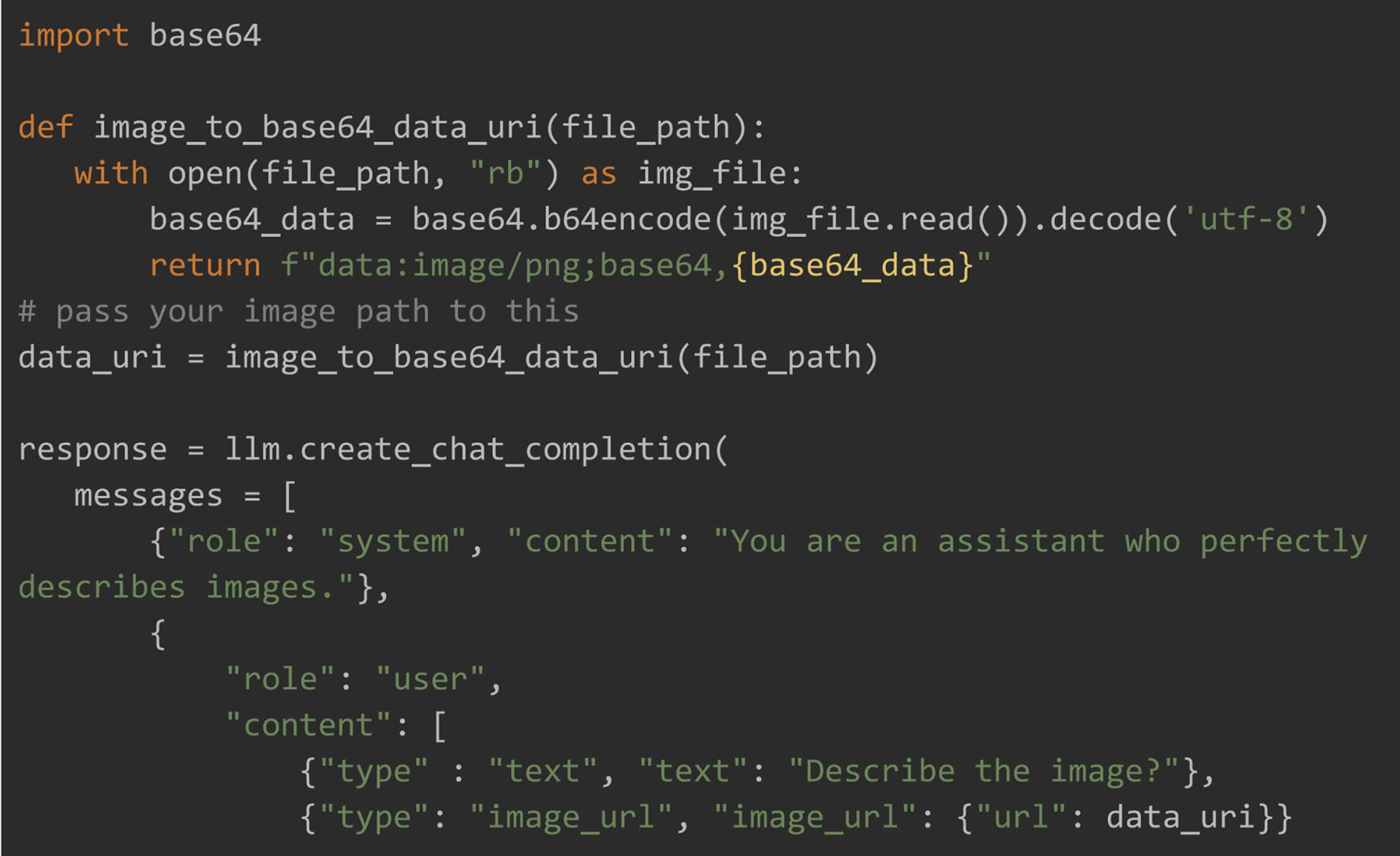
To pass local image to the model, it should be first converted to base64 encoded data and then passed to url parameter.

We have now seen that with LLaMA.cpp, you can run powerful LLMs, in quantized version, right on your local machine — no fancy hardware needed. Whether you’re generating text or diving into multimodal AI with vision models, you’re all set to experiment and build.
